Various Uses of e-Learning Content
e-Learning Initiatives develops ancillary materials for coursework to support credit recognition using the e-learning system with a main focus on videotaping and editing ordinary lectures. However, recent years have seen a greater need for e-learning materials not only as tools for credit recognition but also as ancillary materials for actual classes. This section gives an insight into various uses of e-learning content.
▼A variety of production methods
▼Examples of Content Use
▼Uses and Advantages of e-Learning Content
▼Video and voice analysis by using AI
▼Content Updates, Changes, Successions and Deletions
A variety of production methods
1. Videotaping of ordinary lectures with students (undergraduate/graduate classes)
- All lectures on a course are videotaped as in the past.
- Classes for quizzes and group work need not be videotaped.
- It is also possible to videotape only certain sessions, such as wrap-up lectures.
![]()
Videotaping of all lectures

Not all lectures need to be videotaped.

It is also possible to videotape only certain lectures.
- Lecture videos can also be edited into different sections for broadcast.
- Videos do not need to be 90 minutes long.
- For content that will probably be frequently updated, such as new research outcomes, single sections are advantageous because they can easily be replaced later.
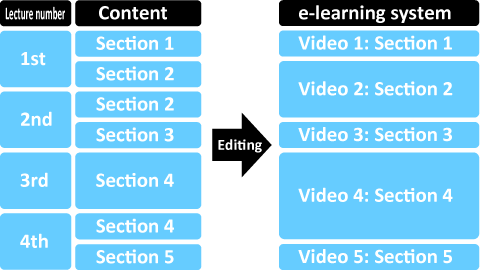
Videos can be edited by section.
2. Videotaping of lectures without students
- L-200 Lecture room may be used as a videotaping studio, and lectures in other rooms can also be videotaped.
- Video can be shot throughout the year and during long holidays (i.e., summer and/or spring break).
- L-200 Lecture room is available for videotaping lectures (90 minutes x 15 lectures) and producing short videos for classwork preparation as well as other ancillary materials.

L-200 Lecture room: recommended as a videotaping studio

Videotaping in other rooms also possible
3. Video production with audio and slide data
- Videos can be produced using audio and slide data.
- L-200 Lecture room can also be used for audio recording. Recording equipment is available for rental.

All CEED needs is sound and slide data.
Examples of Content Use
Outlined below are actual examples of content use.
Example 1: Videotaping of the Japanese version of a regular English-language class as ancillary material

![]()
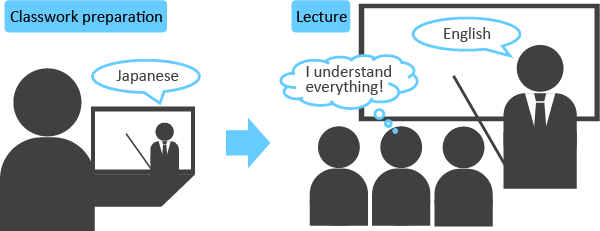
Classwork preparation involving watching Japanese versions of videos for enhanced understanding
Example 2: Production of a short video as ancillary material to be used during lectures

For these reasons, the instructor wanted to create video presentations in advance to show in his classes and allow students to watch them at home.
![]()
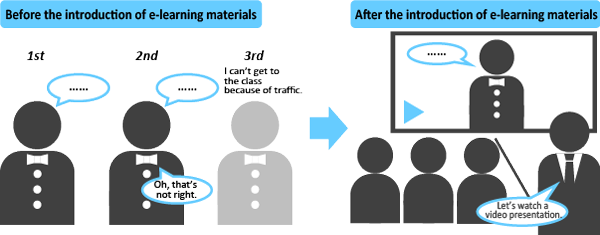
Playback of videotaped presentations as ancillary materials during lectures
Example 3: Videotaping of wrap-up lectures only

![]()

The 5th lecture as a wrap-up for the 1st to 4th lectures, the 10th as a wrap-up for the 6th to 9th lectures, and the 15th as a wrap-up for the 11th to 14th lectures
Example 4: Videotaping for students unable to attend supplementary classes

![]()
Example 5: Development of basic study materials for students taking a course as a minor

![]()
Uses and Advantages of e-Learning Content
Outlined below are examples of e-learning content use other than for credit recognition.
- All e-learning materials are available to support preparations for/review of actual classes and as resources to help students who miss classes due to sickness, bereavement leave, overseas study, internships, job-hunting activities and the like.
- As a general rule, broadcasting begins in the semester following that in which the content is produced. However, students attending actual classes may also be allowed to watch content in the same semester.
Video and voice analysis by using AI
CEED’s e-learning system is provided with the video and voice analysis services by using AI.
*Azure Media Services and Azure Cognitive Services supplied by Microsoft are utilized for these analysis services. For more details on the applicable language and so on, please visit Media Indexer (Microsoft), Translator Text API (Microsoft) and Text to Speech (Microsoft).
- Speech→Text: Automatic translation from voice data to text data.
- Text→Translation: Automatic translation from one language to another.
- [Under development] Text→Speech: Automatic recording of the speech from the text.
- [Under development] Translated text→Speech: Automatic recording of the translated speech from the text.
These services can be used not only for the contents produced by CEED but also for your own videos and voice datas. Please make inquiries using the following application form.
Application form for the video and voice analysis services (Japanese only)
Please refer to the following manuals for the video and voice analysis services.
- 01 CEEDMoodle Manual: A series of flow (Japanese only)
- 02 CEEDMoodle Manual: Subtitle display position (Japanese only)
- 03 CEEDMoodle Manual: Editing a subtitle (Japanese only)
- 04 CEEDMoodle Manual: Subtitle translation (Japanese only)
Content Updates, Changes, Successions and Deletions
- Old or obsolete e-learning materials can be updated. Inform e-Learning Initiatives of the need for an update as soon as possible so that the request can be incorporated into the videotaping schedule. (It is possible to videotape only lectures requiring updates; not all lectures need to be videotaped again.)
- e-Learning Initiatives also responds to requests for partial revisions of videos/reference materials and other changes.
- Instructors departing for reasons such as retirement are asked to allow continued broadcasting of their e-learning materials in viewing only status. However, materials can still be used in an ancillary capacity in coursework for credit recognition in addition to viewing only transmission if both the instructor and the successor permit such usage.
- Instructors wishing to delete content for any reason should contact e-Learning Initiatives.